Woody Species
Woody Species sagemThe Species Production Guides for woody species (prairie shrubs) provide specific information about growing each of these species for seed production.
A printable file (pdf) is also provided on each species page for those needing a print version.
This section is a work in progress. We will continue to add new species guides as they are completed.
Rosa arkansana / prairie rose
- Spiraea alba / white meadowsweet
false indigo bush
false indigo bush sagem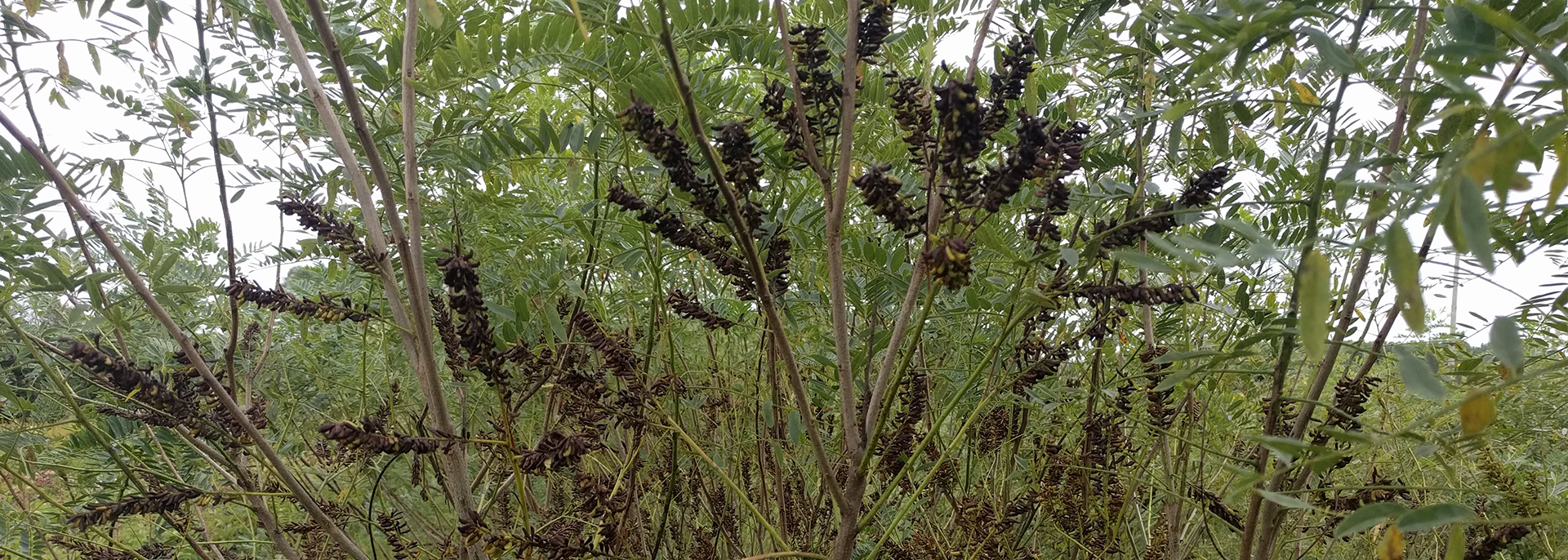
Amorpha fruticosa, L.
Alternate Common Names: false indigo, bastard indigo, river locust, wild indigo, indigo bush, desert false indigo
Scientific Synonyms: Amorpha angustifolia (Pursh) Boynt., Amorpha bushii Rydb., Amorpha croceolanata P.W. Watson, Amorpha curtissii Rydb., Amorpha dewinkeleri Small, Amorpha occidentalis Abrams, Amorpha tennesseensis Shuttlw. ex Kunze, Amorpha virgata Small
Family: legume or pea family (Fabaceae (Leguminosae))
Functional Group: woody species, shrubs
Description
- Life cycle and growth form
Fast-growing, long-lived perennial shrub, spreads by self seeding and suckering, flowers on second-year wood.
Height: 3 -12 ft
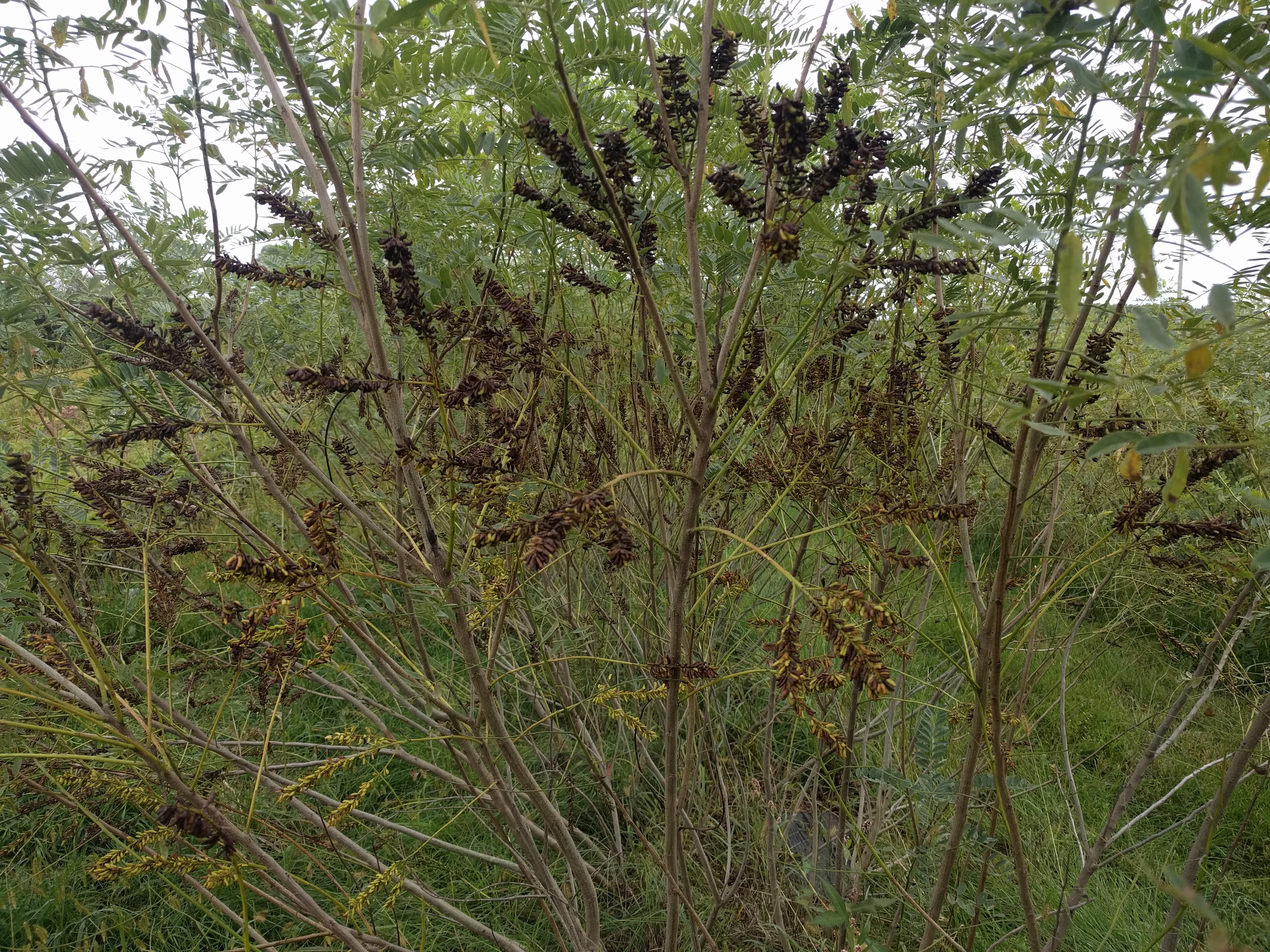

- Leaves and stem
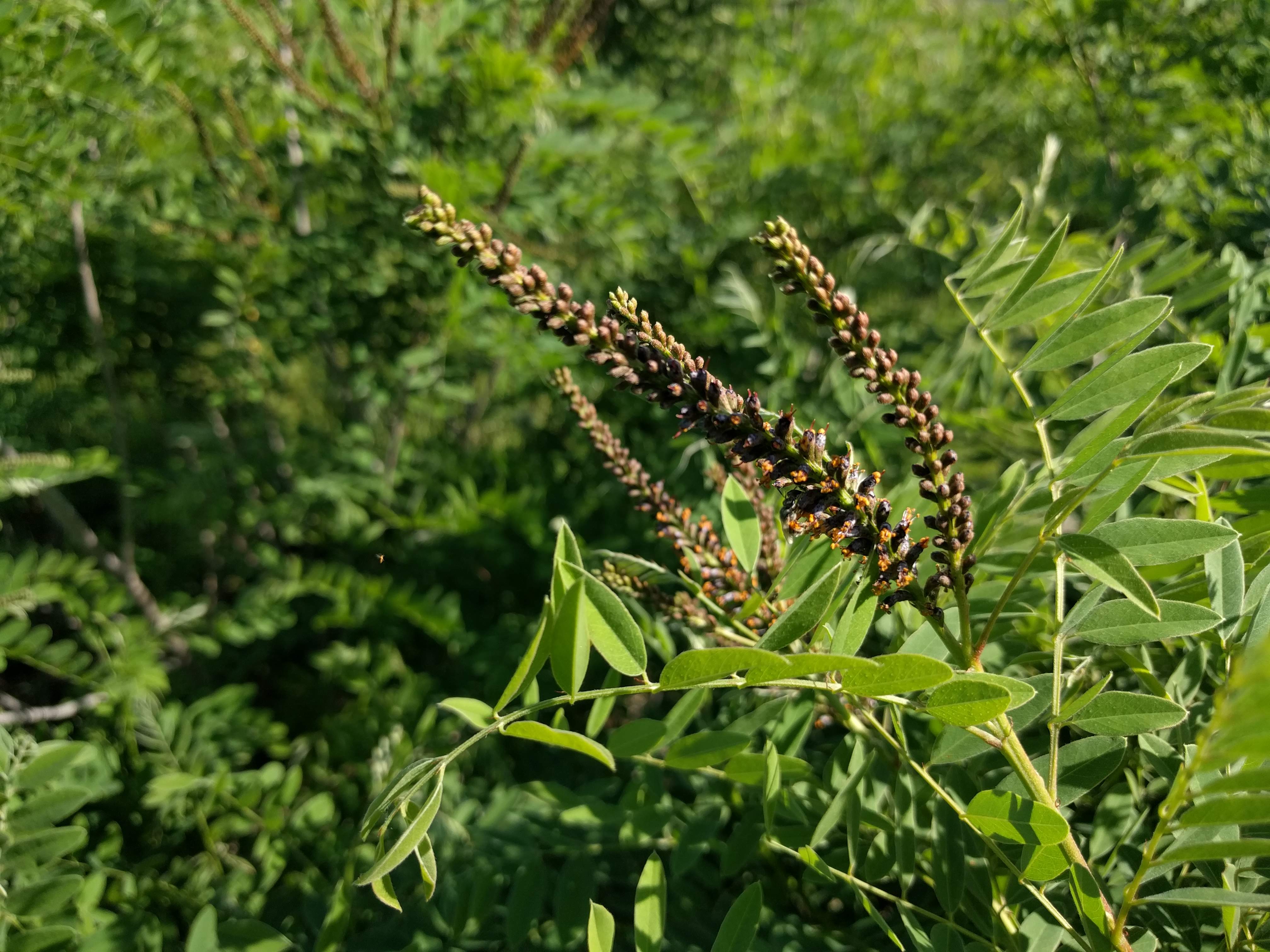

Leaves 4-8 in long, pinnately compound with 11-25 oblong leaflets, alternate arrangement; multi-stemmed shrubs with smooth, gray, woody stems, forming thickets of spreading, cane-like stems that begin sparsely branching at about 3-4 ft in height.
- Flower, fruit and seedhead
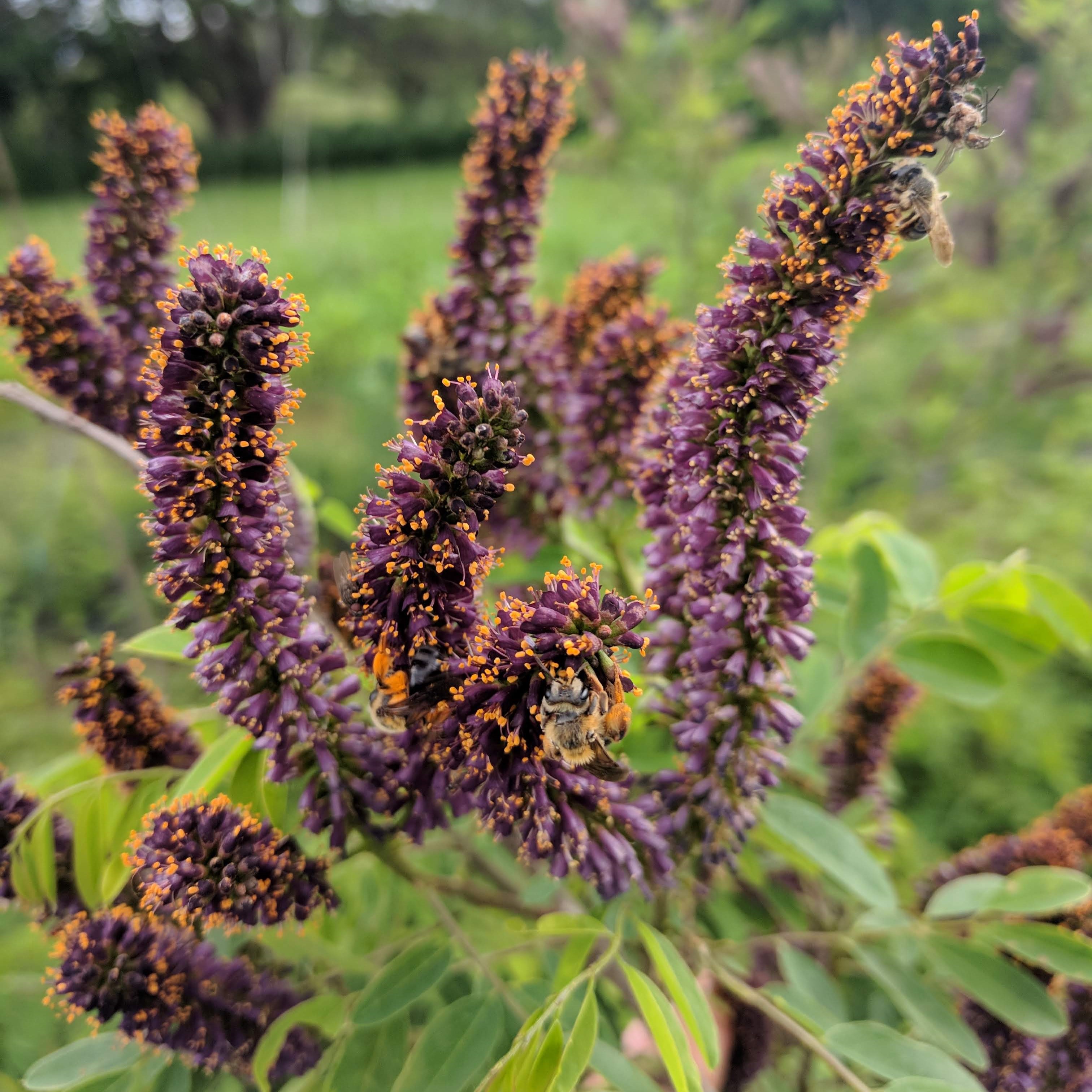
Flower: Irregular, with one slightly enlarged petal (unlike the typical legume flower), deep purple corolla ⅓ in long, with bright orange stamens that stick out prominently; flowers tightly packed in spikelike racemes 3-6 in long (each looking like a tapered bottle brush).
Fruit/seedhead: ¼ in long, tough, leathery seed pods with prominent oil glands, each pod with one seed (sometimes two).

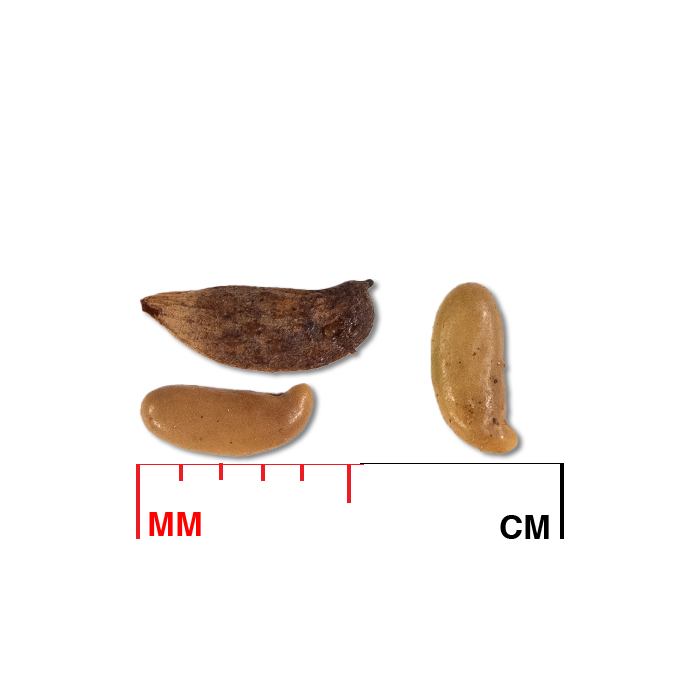
- Seed
Note: Seed produced from unirrigated rows at the TPC had much lower viability (PLS: 16-23%, not included in the typical seed test above).
Seed characteristics
Seeds per ounce: 3,700 (IA NRCS)
Seeds per pound: 77,000 (Woody Plant Seed Manual)
1000 seed weight: 7.76 g (Seed Information Database)
Description: Glossy, light-brown seed resembles a small bean, 4 mm long and 1.5 mm wide, with a slightly hooked end.
Typical seed test
PLS: 90-94%
Purity: 98%
Germination: 31-92%
Dormancy: 0-65%
(based on tests of one lot of commercial seed and one lot produced at the TPC)
- Habitat and range
Habitat: Moist soil; partial to full sun; along river and stream banks, islands, ditches, wet prairies, and seeps; designated a Facultative Wetland species for the Midwest by the USDA. Plants survive for many years in mesic soils without irrigation, but seed yield (and possibly viability) increases with irrigation.
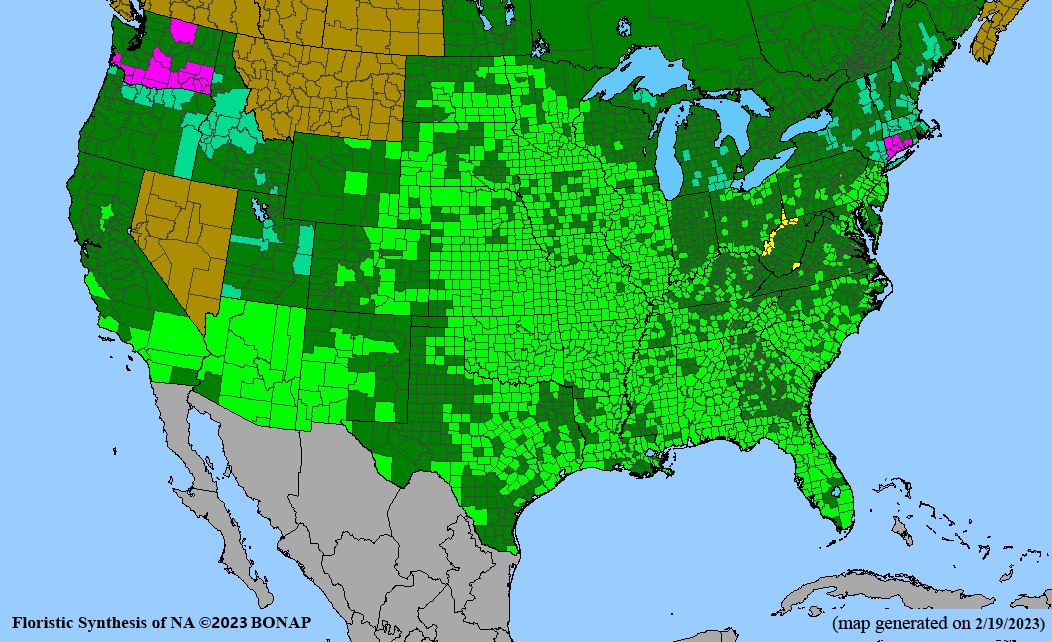
Conservation status: Global- G5, secure; Wyoming- S2, imperiled; West Virginia- S2/S3, imperiled to vulnerable (NatureServe); Listed as a noxious weed or invasive plant in Maine, Rhode Island, New Jersey, New Hampshire, Oregon, and Washington.
General Comments
The dark purple flower spikes with brilliant orange pollen-bearing stamens attract numerous species of native bees in great abundance, along with skippers, other butterflies, and moths. The foliage and pods, when crushed, have an unusual scent, reminiscent of cumin, citrus, and creosote. Aromatic compounds from this species have been investigated as medicines, natural insecticides and insect repellents. The foliage is eaten by larvae of silver-spotted skipper and southern dogface butterflies, larvae of amorpha borer beetles live within the stems and roots, and tiny bruchid beetles feed on the seeds. The long, weakly branched stems have been used in arrow-making and as a foundation for bedding materials by Native peoples. The functions this species provides in restoration include erosion control, streambank stabilization, wildlife cover, and windbreaks, and it shows potential for use in living snow fences.
Recommendations for Seed Production
- Establishment for seed production
Direct seeding
We do not have experience with direct seeding this species for seed production. Widely spaced rows (6 ft or more) are recommended.
Greenhouse
Seed pre-treatment: Start seed pretreatment about 3-4 months before outplanting. Mechanical or chemical scarification is recommended as these seeds have physical dormancy, followed by 10-14 days cold/moist stratification (40°F).
Sowing: Cover seed lightly (¼ in depth) with potting mix; adding a layer of perlite or chick grit to the surface of the soil may help prevent damping off.
Transplanting: Seedlings are ready for transplanting when roots have reached the bottom of the plug and are well-branched, creating a firm plug. Harden off outdoors, then transplant into plasticulture rows with drip irrigation, 2-3 plants per linear foot.
- Stand management
Weeds: Plastic mulch controls weeds in year one. Shrubs grow vigorously and shade out most weeds.
Pests: In very snowy winters, rabbits feed on bark and may girdle stems. Shrubs will resprout but flowering and seed set will be delayed for a year. Deer occasionally browse the tops of plants. Some native insects feed on foliage or within stems/roots, but not at densities that cause production issues. Bruchid beetles feed on developing seeds within pods and can reach significant densities. However, seed yield is still high in “good years” and when rows are irrigated.
Diseases: An unidentified rust fungus causes leaves to appear distorted in some years.
Note: Rows can be cut back to the ground in the dormant season if plants have become too lanky for efficient harvesting. Note that this shrub species does not flower or set seed on first year growth.
- Seed production
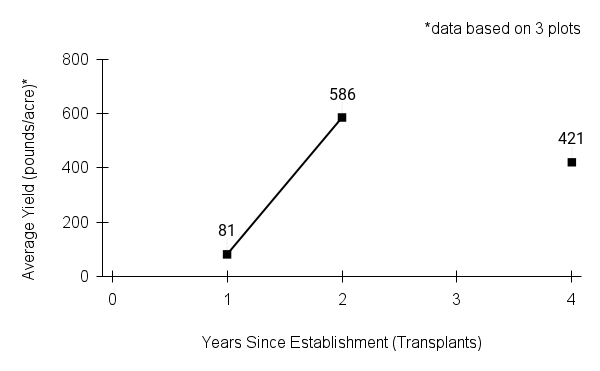 First harvest: Plants flower and set seed one year after transplanting.
First harvest: Plants flower and set seed one year after transplanting.Yield: 80-580 pounds/acre (based on 3 plots)
Stand life: More than 10 years (estimated) for these long-lived shrubs.
Flowering date: June
Seed maturity: October
Harvest date range at TPC (2018-2021): Oct 17 - 31
Recommended harvest method: Strip pods from stalks by hand (wear sturdy gloves). We have not attempted to combine this species due to the woody stems. A more efficient approach might be to cut the fruiting stems onto tarps using a hedge trimmer, then run the material through a stationary combine.
- Seed cleaning and storage
Cleaning process: Pass hand-collected pods through a coarse screen (¼ to ½ inch hardware cloth) to remove sticks. Run through a brush machine with canvas beater bars. Seed pods have oil glands (visible under low magnification) and become very sticky when brushed. Spread oily material on a tarp and dry with a fan for a few days. Material may need to be brushed a second time after drying and before airscreening.
Seed storage: Cool/dry (orthodox) - seed retains viability for 3-5 years at room temperature (Woody Plant Seed Manual).
Released Germplasm
Source Identified material: Natural Selections/Iowa Ecotype Zones 1, 2, 3
NRCS releases: Iowa Covey Germplasm, Illinois Covey Germplasm, Missouri Covey Germplasm, Survivor Germplasm
- References
Bonner, F. T., Karrfalt, R. P., & Nisley, R. G. (Eds.). (2008). Woody Plant Seed Manual. RNGR - Reforestation, Nurseries, and Genetic Resources. https://rngr.net/publications/wpsm
Hilty, J. (2019). False Indigo - Amorpha fruticosa. Illinois Wildflowers. https://www.illinoiswildflowers.info/trees/plants/false_indigo.htm
Kartesz, J.T., The Biota of North America Program (BONAP). 2023. North American Plant Atlas. (http://bonap.net/napa). Chapel Hill, N.C. [maps generated from Kartesz, J.T. 2023. Floristic Synthesis of North America, Version 1.0. Biota of North America Program (BONAP). (in press)]
Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center - The University of Texas at Austin. (2022). Amorpha fruticosa. Plant Database. https://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=amfr
Moore, L. M. (2006). Desert false indigo - Amorpha fruticosa L. Plant Guide. USDA-NRCS National Plant Data Center. https://plants.usda.gov/DocumentLibrary/plantguide/pdf/pg_amfr.pdf
NatureServe. 2024. NatureServe Network Biodiversity Location Data accessed through NatureServe Explorer [web application]. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available https://explorer.natureserve.org/. (Accessed: February 22, 2024).
Newcomb, L. (1977). Shrubs / Leaves Divided. In Newcomb’s Wildflower Guide (pp. 106–107). Little, Brown and Company.
Runkel, S. T., & Roosa, D. M. (2009). Indigo bush. In Wildflowers of the Tallgrass Prairie: The Upper Midwest (2nd ed., pp. 66–67). University of Iowa Press.
University of Georgia - Center for Invasive Species and Ecosystem Health. (n.d.). Indigobush (Amorpha fruticosa) - eddmaps. EDDMapS.org. https://www.eddmaps.org/species/subject.cfm?sub=5086
USDA NRCS National Plant Data Team. (n.d.). Amorpha fruticosa L. USDA plants database. https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=AMFR
Species Guide Updated 3/5/2024
white meadowsweet
white meadowsweet sagem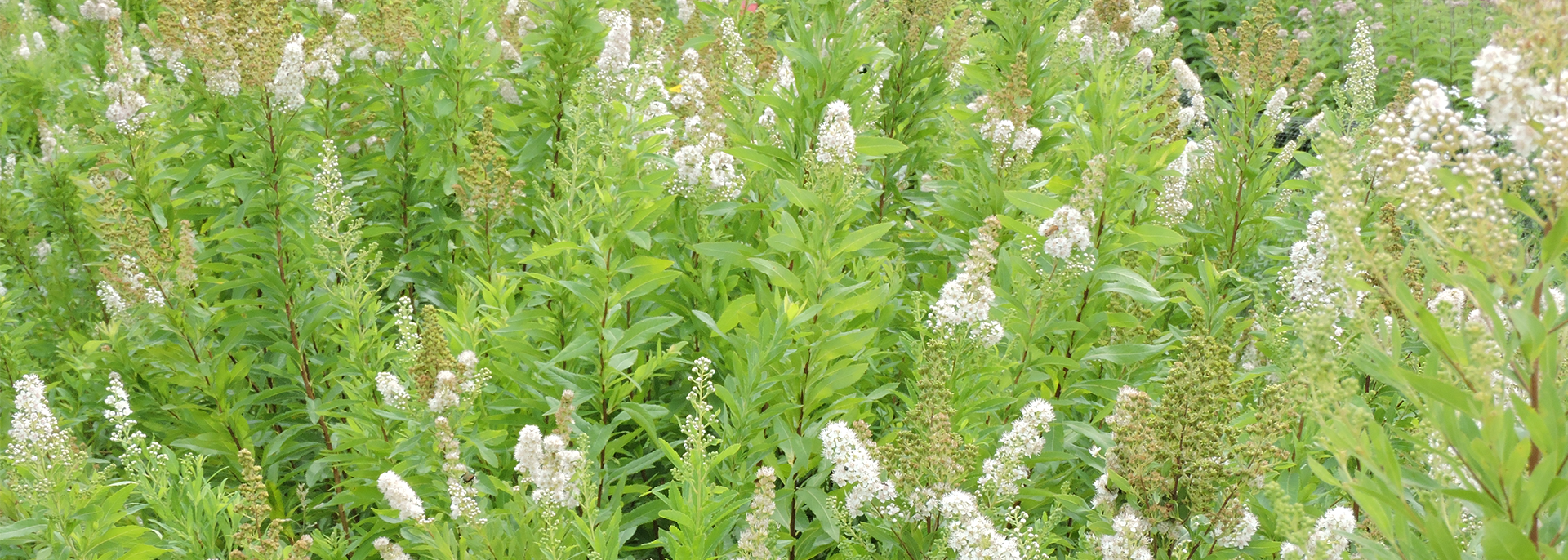
Spiraea alba, Du Roi
Alternate Common Names: meadow sweet, meadowsweet, narrow-leaved meadowsweet, American meadowsweet, pale bridewort, pipestem, queen of the meadows
Family: rose family (Rosaceae)
Functional Group: woody species, shrubs
Description
- Life cycle and growth form
Perennial shrub with woody root system, growing in colonies of slender stems.
Height: 2-4 ft
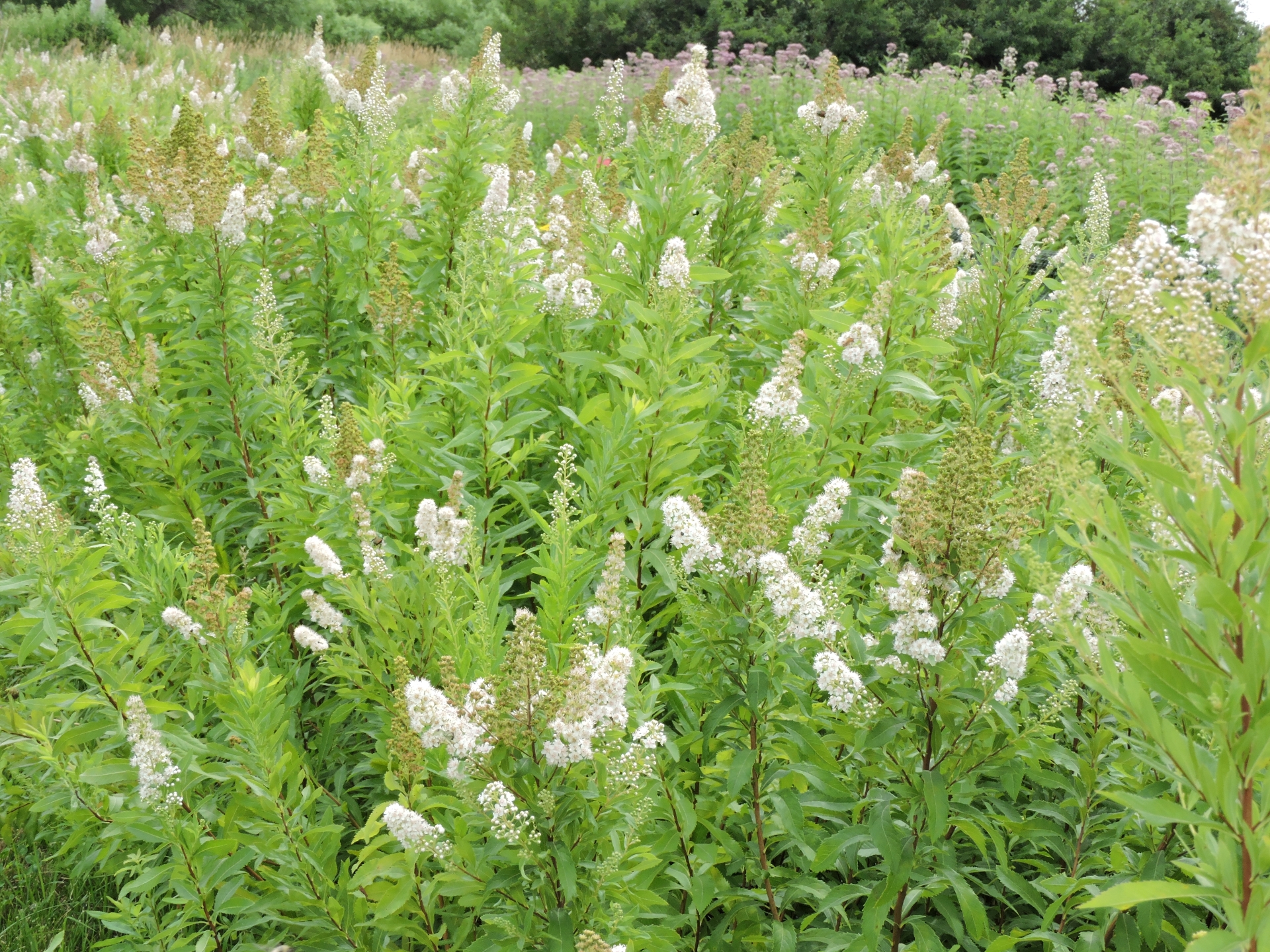

- Leaves and stem

Leaves alternate, mostly hairless, narrowly elliptic, 2-3 in long and ¾ in wide, with finely serrate margins and short petioles; stems smooth, slender, and woody, with few branches, becoming brown with age, multiple stems produced from the same rootstock.
- Flower, fruit and seedhead
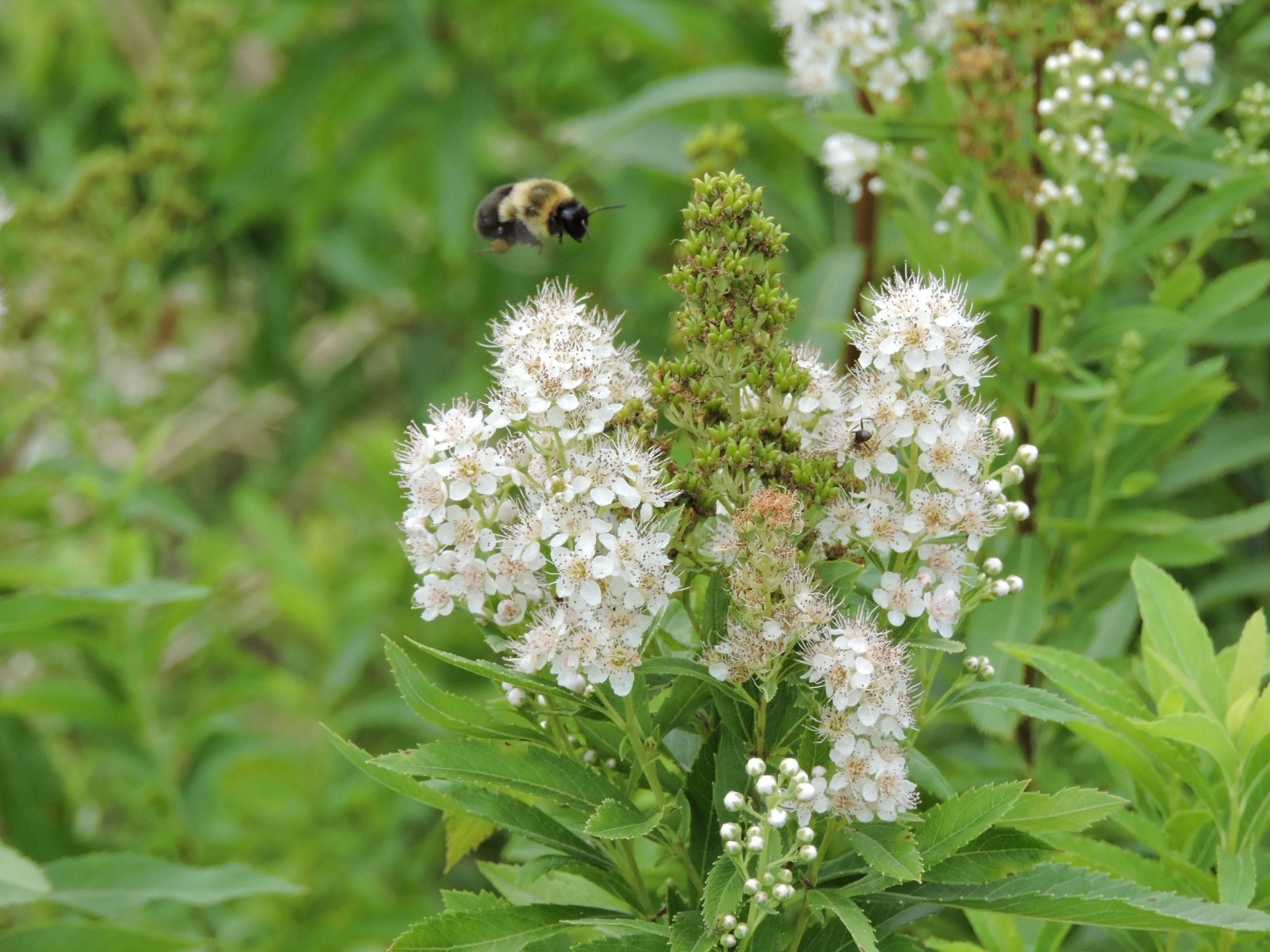
Flower: Radially symmetrical, ¼ in wide flowers are five-parted with white petals, a pink, yellow, or orange center ring, and long stamens that stick out from the flowers; inflorescence is a branched cluster of spikes 2 - 6 in long, each with numerous flowers, blooming from the top down.
Fruit/seedhead: Each flower forms four to six (usually five) dry, reddish-brown fruits (follicles), arrayed in a star-like cluster; each follicle is tough, short-beaked, hairless, and contains 2-5 seeds; ripe follicles split open along one side to release the seeds.

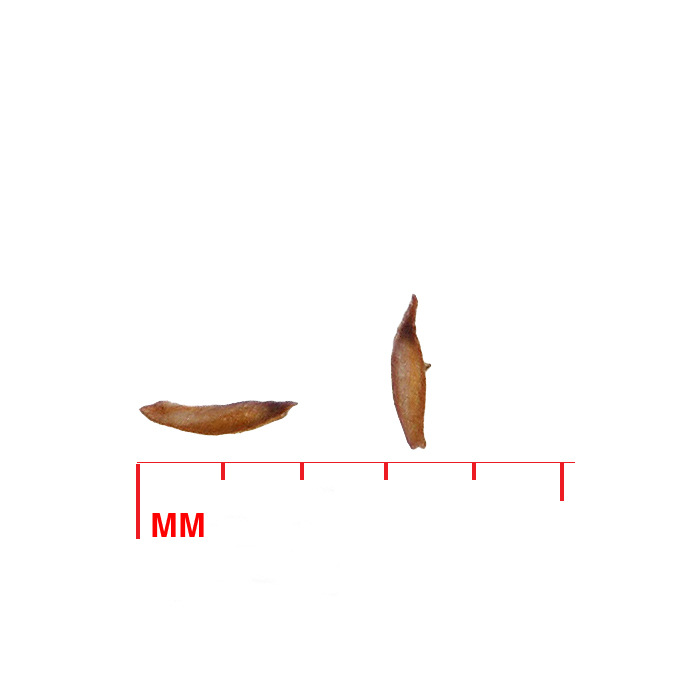
- Seed
Seed characteristics
Seeds per ounce: 300,000 (Prairie Moon)
1000 seed weight: 0.88 g (Seed Information Database)
Description: Slender, banana-shaped seeds are 2 mm long by less than 0.5 mm wide and a rusty orange color.
Typical seed test
TZ-PLS: 53%
Purity: 60%
TZ: 88%
(based on 3 seed lots produced at TPC)
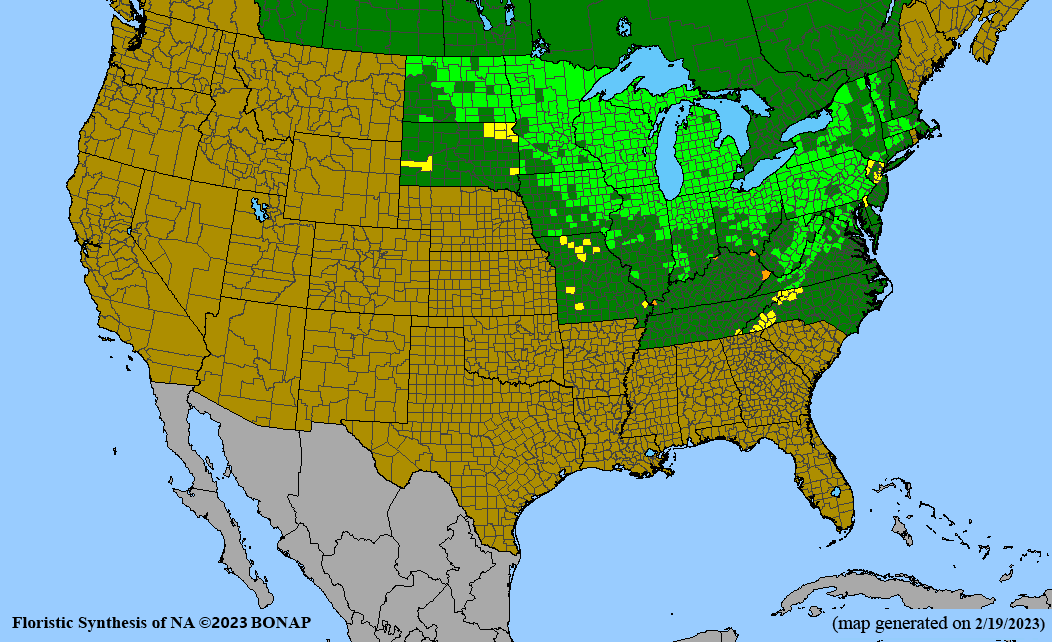
- Habitat and range
Habitat: Grows in moist to wet soil in full sun; found in wet prairies, along streams, bogs, marsh edges, ditches; Facultative Wetland status in Midwest (USDA Plants Database); benefits from irrigation in seed production systems.
Conservation status: Global- G5, secure; Delaware and Tennessee- S1, critically imperiled; North Carolina- S2, imperiled; South Dakota- S3, vulnerable (NatureServe)
General Comments
The long flowering time and abundance of nectar and pollen make this an important food plant for many kinds of bees as well as small butterflies, wasps, beetles, and flies. We have observed the endangered Rusty Patched Bumble Bee visiting the flowers in white meadowsweet seed production plots. The dense colonies of stems provide shelter and nesting habitat for some bird species. The leaves, stems, and/or roots have uses in the traditional medicine and foodways of several Indigenous groups within the plant’s native range. Recommended for use as a low hedge, in perennial borders, wet prairie restorations, and roadside plantings.
Recommendations for Seed Production
- Establishment for seed production
Direct seeding
We do not have experience with direct seeding this species for seed production.
Greenhouse
Seed pre-treatment: 45 days cold-moist stratification.
Sowing: Seeds are small and must be surface-sown; stratified seed germinates quickly (starting 5 days from sowing).
Transplanting: Seedling plugs (2.5 in deep, 73-cell trays) are ready to transplant about 12 weeks from germination. After several weeks in plugs, seedlings benefit from fertilizer application such as a sprinkling of coated fertilizer pellets. Harden off outside, then dibble into a weed barrier in irrigated production rows.
- Stand management
Weeds: Few issues if weed barrier used in planting year; dense foliage shades out most weeds in subsequent years; mow and trim between rows.
Pests: A few stems are affected by dark colored aphids that cause distortion of leaves and growing shoot tips.
Diseases: None noted.
Note: Mow plots down to 4 in during the dormant season every other year to stimulate production of robust new stems.
- Seed production
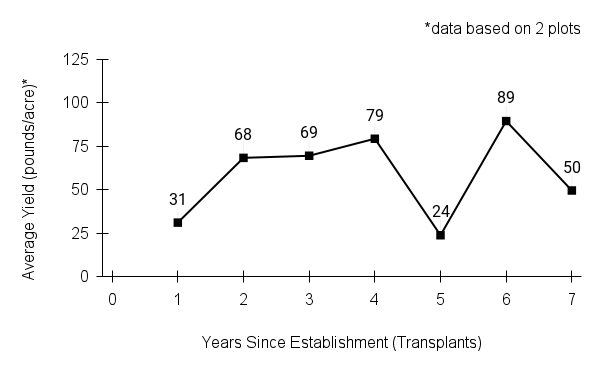 First harvest: second year
First harvest: second yearYield: 25-90 pounds/acre (based on 2 plots)
Stand life: at least 8 years
Flowering date: June - August
Seed maturity: late October - early November
Harvest date range at TPC (2017-2023): Oct 17 - Nov 1
Recommended harvest method: Check plots frequently from mid-October through early November; hand clip or combine when follicles (dry fruits) have split open on most stalks.
- Seed cleaning and storage
Cleaning process: Do NOT use a brush machine. Brushing pulverizes the dried leaves, making it very difficult to extract the fine seed. Hand-clipped material can be beaten in a cloth bag to release seed. Combined or hand collected material can then be treated in the same way: run through ¼ in hardware cloth to remove sticks, then airscreen. If greater purity is desired, passing the cleaned seed through soil sieves can remove residual chopped leaf material.
Seed storage: cool/dry (orthodox)
Released Germplasm
Source Identified material: Natural Selections/Iowa Ecotype Zones 1 and 2
- References
Chayka, Katy. (n.d.). Spiraea alba (White Meadowsweet). Minnesota Wildflowers. https://www.minnesotawildflowers.info/flower/white-meadowsweet
Cochrane, T. S., Elliot, K., & Lipke, C. S. (2014). White Meadowsweet. In Prairie Plants of the University of Wisconsin-Madison Arboretum (3rd ed., p. 314). University of Wisconsin-Madison Arboretum.
Hilty, J. (2019). Meadowsweet - Spiraea alba. Illinois Wildflowers. https://www.illinoiswildflowers.info/wetland/plants/meadowsweet.htm
Kartesz, J.T., The Biota of North America Program (BONAP). 2023. North American Plant Atlas. (http://bonap.net/napa). Chapel Hill, N.C. [maps generated from Kartesz, J.T. 2023. Floristic Synthesis of North America, Version 1.0. Biota of North America Program (BONAP). (in press)]
NatureServe. 2024. NatureServe Network Biodiversity Location Data accessed through NatureServe Explorer [web application]. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available https://explorer.natureserve.org/. (Accessed: February 28, 2024).
Runkel, S. T., & Roosa, D. M. (2009). Meadow sweet. In Wildflowers of the Tallgrass Prairie: The Upper Midwest (2nd ed., pp. 142–143). University of Iowa Press.
USDA NRCS National Plant Data Team. (n.d.). Spiraea alba Du Roi. USDA plants database. https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=SPAL2
Species Guide Updated 3/5/2024